By Donald Voltz, MD, Aultman Hospital, Department of Anesthesiology, Medical Director of the Main Operating Room, Assistant Professor of Anesthesiology, Case Western Reserve University and Northeast Ohio Medical University.
A board-certified anesthesiologist, researcher, medical educator, and entrepreneur. With more than 15 years of experience in healthcare, Dr. Voltz has been involved with many facets of medicine. He has performed basic science and clinical research and has experience in the translation of ideas into viable medical systems and devices.
Thanh Tran, CEO of Zoeticx Inc. also contributed.
According to data published on HealthIT.gov, 173 health IT vendors are supplying certified EHR products to more than 4,500 hospitals. Despite wide penetration of EHR’s in hospitals, clinics and physician offices, access to patient information between systems continues to plaque our healthcare system. From a physician’s perspective, we have a duty to provide the best care to addresses our patients’ health needs with the least possible risks of adverse events.
We can look at the EHR implementation history from a similar perspective to collect, store and allow for timely, accurate and appropriate access to patient health information from any and all healthcare providers who require the information to meet the needs of their patients. Medicine is a data intensive field involved in risk assessment, reduction and/or mitigation of risks during the course of treatment. At the same time it must be cognizant of the limited resources available and the costs incurred by patients, employers and the entire health system.
No matter what area of healthcare or what role one plays in the care of our patients, we all play a role in the art and science of medicine as well as the economic implications of our decisions. The same requirements and limitations placed on healthcare providers from the care delivery side are impacting all providers on the technology side with the requirements put in place for EHR use.
The vast majority of healthcare providers are not tech savvy. Many have worked very hard to overcome their discomfort with computer charting and other technical requirements that are now omnipresent in medicine. Access to patient information, not only that which is individually collected, but all of the information collected across a care continuum not only adds value and accuracy to the decisions made in the management of a patient, but also impacts the cost of care to the patient and system.
We have learned a great deal about technology from other industries that has direct implications for healthcare. Competitive advantage does not come directly from the implementation of technology, but instead from the information that is enabled by the technology. EHR’s alone will not solve the needs of our patients or our providers. But they do have the potential to greatly impact the way care is delivered, and help to realize the value contained in our patients’ health data, both for the acute illness as well as the chronic medical conditions that can span a lifetime. The question of how to best realize the value contained in the rapidly expanding database is still opened for debate.
Health Data Requires Connecting the Pieces
The greatest value promised from health data comes from connecting the pieces. Enabling real-time access to patient data by the providers who are making decisions in the office, the emergency department, on the wards or in the operating room is not a luxury today, but a requirement for patient safety, quality and cost effective care. To do this requires one of two approaches, collect every piece of patient health data in a single or tightly coupled set of databases or develop an interface to the various EHRs, established and yet to be developed. The decision cannot be taken lightly given inherent risks as well as the unforeseen consequences that result as we scale data.
Cost and risk are two of the major determinants of how we solve the data access problem for healthcare. A third, often downplayed issue, is the ability to scale and respond to new technology. In the era of big data, one is easily fooled about the integrity, providence and accuracy when the data is moved from one system to another.
Knowing where a piece of information originated from can be the difference between catching and addressing an issue before a negative outcome or missed diagnosis is made. Solving the healthcare interoperability challenge by establishing large data warehouses where all patient data eventually is stored leads to duplication of data. This is a cumbersome risk prone solution where issues are often not realized until they are questioned at the point of care where accuracy and trust in the data source is a requirement.
Middleware More than Simple System Glue
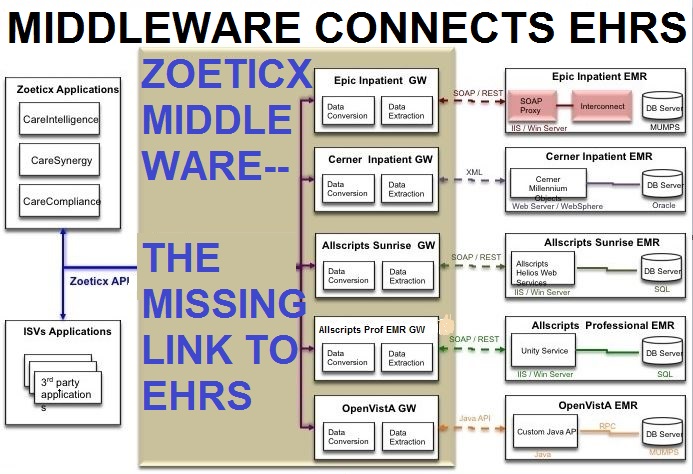
Middleware, software that serves to connect previously disconnected systems, has shown value in many data intensive sectors outside of healthcare. Middleware goes beyond the simple “gluing” of two disconnected systems together. It often serves to synergize and get more than the sum of the two systems together.
The thought of expanding the functionality of EHR’s is an attractive one for many in healthcare. Technology at the scale of EHR’s takes time to advance. There is no question establishing and maintaining a robust, secure and fault-tolerant database back end is an absolute requirement for EHR systems. This focus slows the ability to add additional features that are required by patients, providers, administrators, and leaders in healthcare.
Zoeticx, a developer of EHR middleware, has developed such a platform that has already been demonstrated to go far beyond the limitations present in EHR’s. Adding additional functionality to patient data has been accomplished with a seamless connection to disparate EHR systems. An additional benefit of this technology is that front-line providers no longer need to worry about accessing many different systems to manually utilize the data for patient care. In addition, the Zoeticx open API brings the ability to develop health IT solutions once and deploy to various EHR’s at a fraction of the cost and with a much reduced amount of risk than doing the same development directly on top of the EHR code base.
Employing a middleware architecture has been shown to reduce risk as well as cost of development, but this is not without critics. Opponents of middleware raise concerns about having to learn the middleware development platform before you see benefits of the platform.
With respect to EHR’s, non-vendor development is not possible or scalable. Although vendors with high market penetration have introduced API’s and development platforms for their systems, development requires new strategies, code and resources for each system. This alone limits widespread implementation of solutions that sit on top of EHR systems or access health data stored in their databases.
Middleware Enables a User Interface to be Standardized Across EHR Systems
A well designed middleware architecture allows a user interface development to be easily standardized across EHR systems to provide visual consistency for healthcare providers, something that has been demonstrated to aid in safety and efficiency. It also solves specific needs at a fraction of the cost required for development for each EHR platform.
Increasingly, organizations in all sectors are realizing the benefits of software, platforms, and architecture as services significantly decreasing business costs. No longer does a company have to do all of the development themselves, but instead are able to rely on off the shelf applications to solve their problems while allowing for middleware to connect the various systems where data resides. Middleware brings an application agnostic approach to connect EHR’s to one another while allowing for specific development to enhance the significant investment by hospitals, health systems and physicians. The approach also allows for scaling, something that centralized or federated HIE’s will continue to have issue with in solving and dealing with data access.
We are still early in the overall lifecycle of EHR’s. Although implementation has been widespread through government incentives, we are still struggling to find efficient and effective ways to utilize these systems. The search for high quality and effective patient care, along with developing solutions to meet the needs of patients so they become engaged with their data and their care still continues.
These issues will require the creative and innovative connection of data to bring meaning and insight into the data. Middleware allows for the spreading standard of SaaS as a mindset for software. The benefits are great while preserving value on the infrastructure already in existence. As we have seen in the IT and financial industries, middleware has transformed technology to bring about uses of data to solve problems. There is no question middleware will do the same for healthcare.