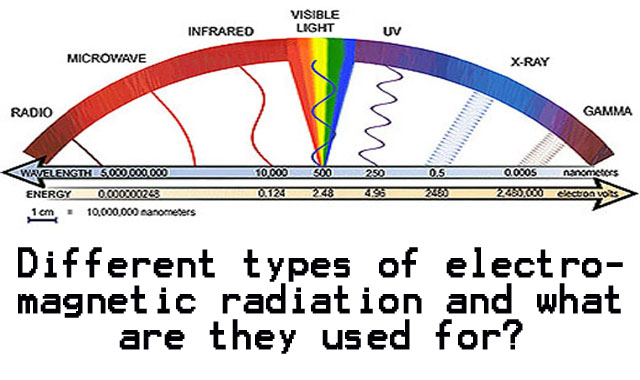
Electromagnetic radiation, or EMR, includes all of the types of energy that can be seen, felt or recorded. Visible light is an example of EMR, and visible light, reflecting off objects enables us to see those objects. Other forms of EMR, such as X-rays and gamma rays, cannot be seen by the naked eye and can be dangerous to humans. EMR is measured in wavelengths, and the shorter the wavelength, which is the distance of the trough between two high points in the EMR wave, the greater the energy used to create the radiation.
Visible Light
The light we see, reflected off objects, has a wavelength measured in nano-meters, or nm for short. A nano-meter is one billionth of a meter. The light that we can see with our own eyes is known as the visible spectrum, and varies from person to person, depending on the sensitivity of a person’s eyes. The visible spectrum is in the range of 380nm to 750nm, although the Harvard University website states that the astronomical range for visible light is 300nm to 1,000nm.
Radio Waves
Radio waves have a much greater wavelength than visible light. Radio waves are the ones we create to transmit radio and television signals through the atmosphere. AM, or amplitude modulation radio waves, are longer than FM, or frequency modulation radio waves, and are better at bending around large objects, meaning that they are useful for transmissions in mountainous regions. AM wavelengths can be measured in hundreds of meters, while FM wavelengths run to just over a hundred meters. FM signals usually produce better sound quality, because FM signals are less susceptible to interference from other EMR waves, such as those made by overhead cables or passing vehicles.
Ultra Violet Light
Ultra Violet light, or UV light, is the light that causes sunburn on human skin. In our solar system, most of the UV light that reaches Earth is created by the hot gas of the sun. The Earth’s atmosphere absorbs most of the UV light that reaches it, in a layer of the upper atmosphere known as the ozone.
Infrared
Infrared light has a wavelength that is longer than that of standard red light, and although considered part of the red color spectrum, infrared wavelengths are still much shorter than, for example, radio waves. Infra-red waves occur in the range from 1,000nm to a millimeter in length. Infrared radiation is created by objects with a temperature of less than 1,340 degrees Fahrenheit, or 1,000 degrees Kelvin. Human beings, with body temperatures of 98.6 degrees Fahrenheit, give off infrared radiation, and this is what is seen when you look through night-vision goggles to see people through the darkness.
X-rays
It takes a high output of energy to create X-rays. X-rays occur in the 0.01 to 10nm range. X-rays used to create photographs of bones in the human body are created at wavelengths of about 0.012nm, which is near the shortest limit of the X-ray spectrum. X-rays at this wavelength will not penetrate through bone, but will penetrate human tissue. The resulting shows the area of bone that was photographed. Over-exposure to X-rays is harmful to humans, so people working with X-rays have to take precautions to remain shielded from the radiation created.
Gamma Rays
Gamma rays need extremely high sources of energy to create them. According to the Harvard University website, gas at a temperature of a billion degrees is needed, so that solar flares and lightning strikes can be sources of gamma radiation. Nuclear explosions also generate gamma rays, and gamma rays have wavelengths of less than 0.01nm. Gamma rays can penetrate human tissue, and even bones, and are extremely harmful to humans.