Social determinants of health (SDoH) significantly influence patient outcomes, yet their documentation is frequently incomplete or absent in the structured data of electronic health records (EHRs). The utilization of large language models (LLMs) holds promise in efficiently extracting SDoH from EHRs, contributing to both research and clinical care. However, challenges such as class imbalance and data limitations arise when handling this sparsely documented yet vital information.
In our investigation, we explored effective approaches to leverage LLMs for extracting six distinct SDoH categories from narrative EHR text. The standout performers included the fine-tuned Flan-T5 XL, achieving a macro-F1 of 0.71 for any SDoH mentions, and Flan-T5 XXL, attaining a macro-F1 of 0.70 for adverse SDoH mentions. The incorporation of LLM-generated synthetic data during training had varying effects across models and architectures but notably improved the performance of smaller Flan-T5 models (delta F1 + 0.12 to +0.23).
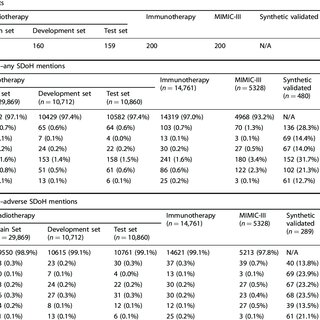
Our best-fine-tuned models outperformed zero- and few-shot performance of ChatGPT-family models in their respective settings, except for GPT4 with 10-shot prompting for adverse SDoH. These fine-tuned models exhibited a reduced likelihood of changing predictions when race/ethnicity and gender descriptors were introduced to the text, indicating diminished algorithmic bias (p < 0.05). Notably, our models identified 93.8% of patients with adverse SDoH, a significant improvement compared to the mere 2.0% captured by ICD-10 codes. These results highlight the potential of LLMs in enhancing real-world evidence related to SDoH and in identifying patients who could benefit from additional resource support.