A new approach that distills deluges of genetic data and patient health records has identified a set of telltale patterns that can predict a person’s risk for a common, and often fatal, cardiovascular disease, according to a new study from the Stanford University School of Medicine.
Although the method, which uses a form of artificial intelligence called machine learning, has so far only been used to predict the likelihood of this particular condition — called abdominal aortic aneurysm, or AAA — it’s proof that such an approach could decipher the molecular nuances that put people at risk for just about any complex genetic disease.
“Right now, genome sequencing is starting to make its mark,” said Michael Snyder, PhD, professor and chair of genetics at Stanford. “It’s being used a lot in cancer, or to solve mystery diseases. But there’s still a big open question: How much can we use it for predicting disease risk?”
It turns out, quite a bit.
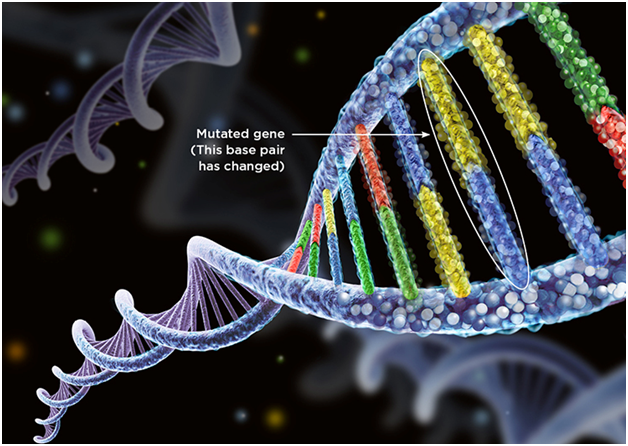
Typically, researchers and health care providers use genetic testing to look for DNA sequences that may correspond to an increased risk for a particular illness. Mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, for instance, may signal an increased risk of breast cancer. But the method that Snyder and his colleagues developed doesn’t work like that. It’s not looking for one standout gene or mutation; it’s looking for a slew of complex mutational patterns, and how those genetic errors play into a person’s health and risk for disease.
The method seeks to identify any likely disease-causing culprits in an “agnostic” manner, meaning that it combs through an onslaught of genetic information from patients with AAA, looking for commonalities. This, Snyder said, is the key to unraveling any number of genetic diseases. It’s not often the case that one, two or even a handful of genes take sole responsibility for a condition. Far more likely is that it’s a whole bunch of them. The idea is that it takes a village to cause a disease, and by using this new method, those villagers can be identified.
The study was published Sept. 6 in Cell. Snyder and Philip Tsao, PhD, professor of medicine, share senior authorship. Instructor Jingjing Li, PhD; research manager Cuiping Pan, PhD; and postdoctoral scholar Sai Zhang, PhD, are the lead authors.
Often diagnosed at death
AAA afflicts upward of 3 million people every year and is the 10th-leading killer in the United States. Patients with AAA have an enlarged aorta, the main artery of the body, which slowly balloons over time until, in the worst of cases, it ruptures. To make matters worse, these types of aneurysms rarely show symptoms. So in many cases, the condition silently escalates, which is in part what makes it so dangerous.
Yet AAA is pretty amenable to behavioral change. Things like smoking and high blood pressure intensify the condition, while higher levels of HDL, or “good” cholesterol, help decrease the risk. So, if people know they are at risk early on, they can ideally adjust their lifestyle to avoid exacerbation or onset altogether.
“What’s important to note about AAA is that it’s irreversible, so once your aorta starts enlarging, it’s not like you can un-enlarge it. And typically, the disease is discovered when the aorta bursts, and by that time it’s 90 percent lethal,” said Snyder, the Stanford W. Ascherman, MD, FACS, Professor in Genetics. “So here’s this irreversible disease, no way to predict it. No one has ever set up a predictive test for it and, just from a genome sequence, we found that we could actually predict with about 70 percent accuracy who is at high risk for AAA.” When other details from electronic patient records were added, like whether a patient smoked and his or her cholesterol levels, accuracy increased to 80 percent, Snyder said.
The method Snyder and his team devised relies on an algorithm they call the Hierarchical Estimate From Agnostic Learning, or HEAL, which analyzed genomic data from 268 patients with AAA and scanned the mass of information for any genes that were found to be mutated across the population. The algorithm identified 60 genes that were hypermutated in the AAA patients. Some genes played roles in blood-vessel function and aneurysm development — a nod to HEAL’s accuracy — but others, more surprisingly, were associated with regulation of immune function, revealing that the mutational landscape of this disease is complex, involving niches of physiology that weren’t necessarily expected.
The team further confirmed their findings using HEAL in a control group, double-checking that the AAA-related mutational patterns were not seen among 133 healthy individuals. And indeed, there was no significant overlap.
“HEAL could, therefore, uncover new research directions and potential therapeutic targets for devastating diseases such as AAA,” said Tsao, who is also the director of the Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Epidemiology Research and Information Center for Genomics.
For other diseases with a genetic component
The key, Snyder said, is that the findings were entirely unbiased. The researchers didn’t say, “We think gene X, Y and Z might play a role in AAA.” They fed the genetic information into HEAL and asked if there were genes or sets of genes that were enriched for mutation. “We let machine learning figure it out, and that’s something that, to our knowledge, has never been done before,” Snyder said.
Even for diseases that have these big “red flag” genomic markers, HEAL could offer a leg up, Snyder said. “For example, in familiar cases like breast cancer, for which we know of specific ‘culprit’ genes, you have to remember that these genes — BRCA1, BRCA2 and a couple others — only explain about 30 percent of the genetics of the disease,” Snyder said. “That means 70 percent is still unexplained. There are probably multiple genes and mutations involved, and that’s where we think HEAL may kick in big time.”
In their next phase of work, Snyder and his group are looking into using HEAL to detect the elusive genetic underpinnings of preterm birth and autism.
“I see a future in which everyone will be born with their genome sequenced, or shortly thereafter,” Snyder said. “Both your single-gene and your complex disease risk will be used to predict your overall disease risk, and then you can take action based on that information.”
The work is an example of Stanford Medicine’s focus on precision health, the goal of which is to anticipate and prevent disease in the healthy and precisely diagnose and treat disease in the ill.
Other Stanford authors of the study are Joshua Spin, MD, PhD, clinical assistant professor of cardiovascular medicine; life science research assistant Alicia Deng; professor of medicine Lawrence Leung, MD; and Ronald Dalman, MD, professor of vascular surgery.
Snyder and Tsao are members of Stanford Bio-X and the Stanford Child Health Research Center. Snyder is also a member of the Stanford Cancer Institute and the Stanford Neurosciences Institute. Snyder and Tsao are members of the Stanford Cardiovascular Institute.
The research was funded by National Institutes of Health (grants CEGS 5P50HG00773504, 1P50HL083800, 1R01HL101388, 1R01HL122939 and S10OD020141), the University of California and the Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development.
Stanford’s Department of Genetics also supported the work.